The Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipation Monitoring (QCM-D) Technique Applied to the Study of Membrane-Active Peptides
 Graphical Abstract: CSIRO
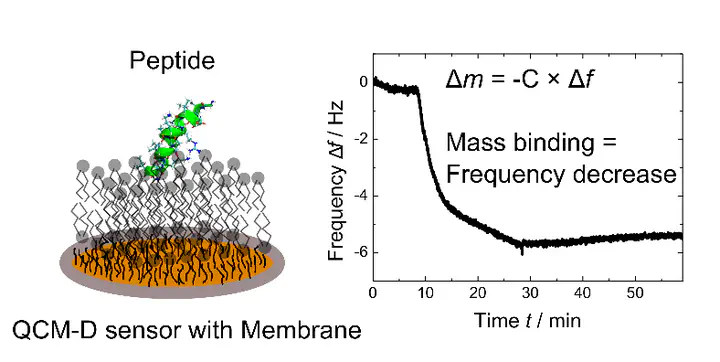
Graphical Abstract: CSIROAbstract
Membrane-active peptides, such as antimicrobial, amyloidogenic or cell-penetrating peptides fulfil complex functions in organisms and have been extensively studied. Antimicrobial peptides offer future opportunities as new antibiotics while amyloidogenic peptides are typically studied in the context of neurodegenerative diseases. Biomembranes play a crucial role as an interface for the action and/or delivery of these peptides. A quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring (QCM-D) offers a tool to study peptide-membrane interactions in vitro, label-free, in real-time and with nanogram sensitivity in solution. This article reports the capabilities of QCM-D for the study of membrane-active peptides.
Type
Publication
Australian Journal of Chemistry